The rise of generative AI and Large Language Models (LLMs) like ChatGPT has disrupted digital practices. More companies choose to deploy applications integrating these language models, but this integration comes with new vulnerabilities, identified by OWASP in its Top 10 LLM 2025 and Top 10 for Agentic Applications 2026. Faced with these new risks and new regulations like the AI Act, specialized solutions, named guardrails, have emerged to secure interactions (by analysing semantically all the prompts and responses) with LLMs and are becoming essential to ensure compliance and security for these applications.
The challenge of choosing a guardrails solution
As guardrails solutions multiply, organizations face a practical challenge: selecting protection mechanisms that effectively reduce risk without compromising performance, user experience, or operational feasibility.
Choosing guardrails is not limited to blocking malicious prompts. It requires balancing detection accuracy, false positives, latency, and the ability to adapt filtering to the specific context, data sources, and threat exposure of each application. In practice, no single solution addresses all use cases equally well, making guardrail selection a contextual and risk-driven decision.
An important diversity of solutions
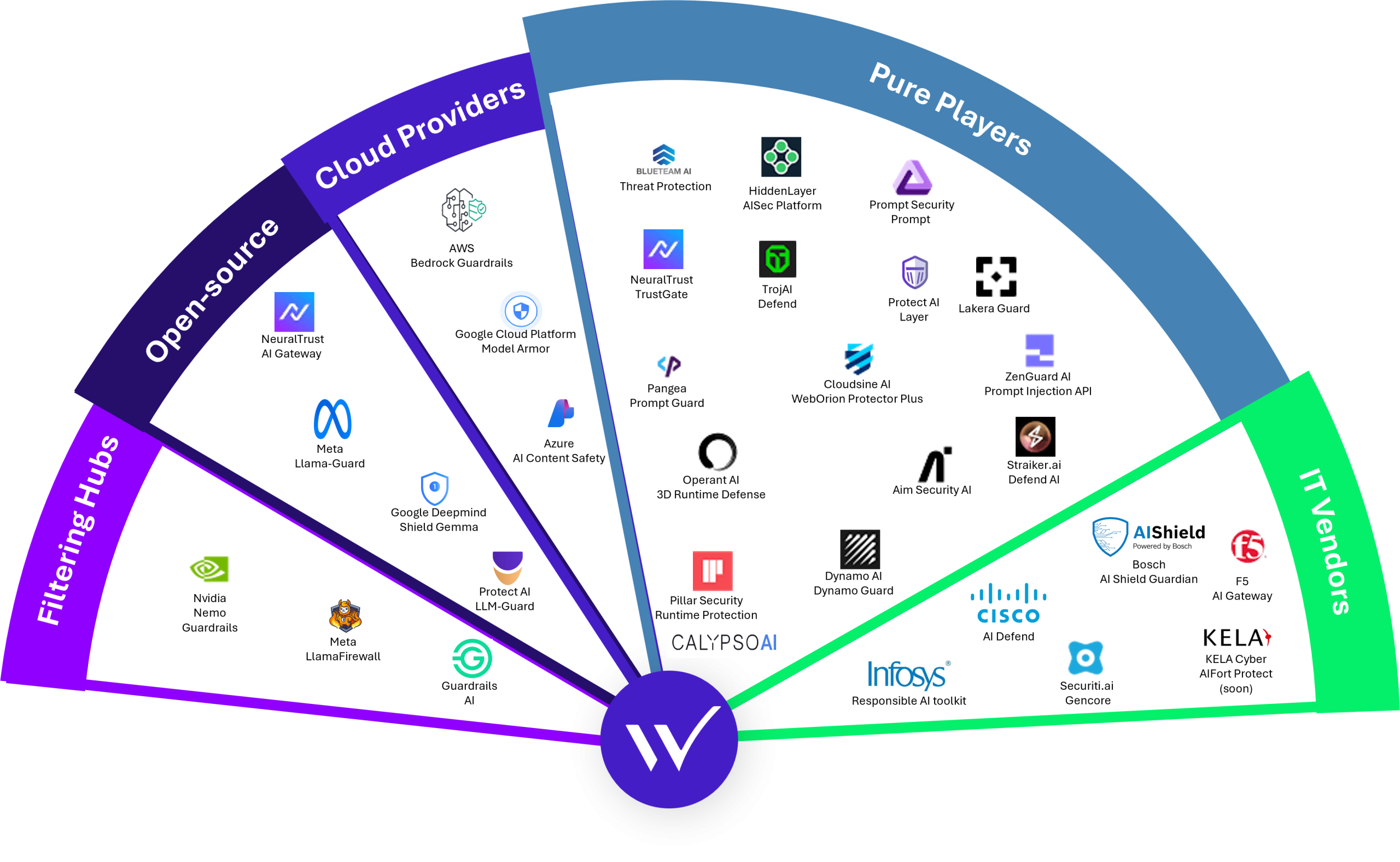
In 2025, the AI security and LLM guardrails landscape experienced significant consolidation. Major cybersecurity vendors increasingly sought to extend their portfolios with protections dedicated to generative AI, model usage, and agent interactions. Rather than building these capabilities from scratch, many chose to acquire specialized startups to rapidly integrate AI-native security features into their existing platforms, such as SentinelOne with Prompt Security or Check Point with Lakera.
This trend illustrates a broader shift in the cybersecurity market: protections for LLM-based applications are becoming a standard component of enterprise security offerings, alongside more traditional controls. Guardrails and runtime AI protections are no longer niche solutions, but are progressively embedded into mainstream security stacks to support enterprise-scale AI adoption
The main criteria to choose your guardrails
With so many guardrails’ solutions, choosing the right option becomes a challenge. The most important criteria to focus on are:
- Filtering effectiveness, to reduce exposure to malicious prompts while limiting false positives
- Latency, to ensure a user-friendly experience
- Personalisation capabilities, to adapt filtering to business-specific contexts and risks
- Operational cost, to support scalability over time
Key Results & Solutions Profiles
To get an idea of the performances the guardrails in the market, we tested several solutions across these criteria and a few profiles stood out:
- Some solutions offer rapid deployment and effective baseline protection with minimal configuration, making them suitable for organizations seeking immediate risk reduction. These solutions typically perform well out of the box but provide limited customization.
- Other solutions emphasize flexibility and fine-grained control. While these frameworks enable advanced filtering strategies, they often exhibit poor default performance and require significant configuration effort to reach good protection levels.
As a result, selecting a guardrails solution depends less on raw detection scores and more on the expected level of customization, operational maturity, and acceptable setup effort.
Focus on Cloud Providers’ guardrails
As most LLM-based applications are deployed in cloud environments, native guardrails offered by cloud providers represent a pragmatic first layer of protection. These solutions are easy to activate, cost-effective, and integrate seamlessly into existing cloud workflows.
Using automated red-teaming techniques, we observed that cloud-native guardrails consistently blocked most of the common prompt injection and jailbreak attempts. The overall performance of the guardrails available on Azure, AWS and GCP were similar, confirming their relevance as baseline protection mechanisms for production workloads.
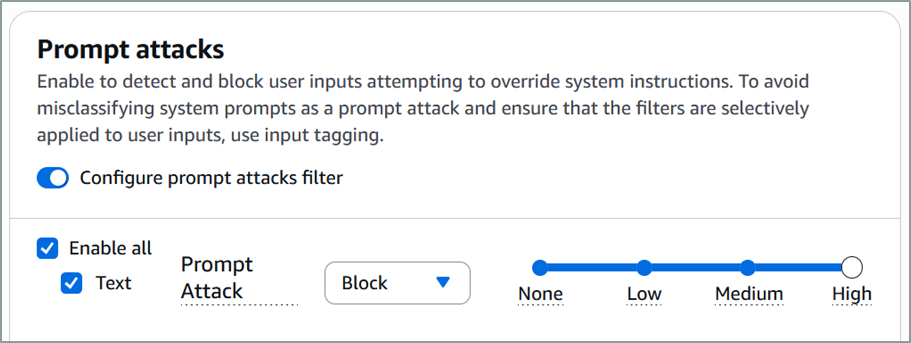
Sensitivity Configuration
The configuration of several of the Cloud provider’s solutions allows us to set a sensitivity level to the guardrails configured in order to adapt the detection to the required level for the considered use-case.
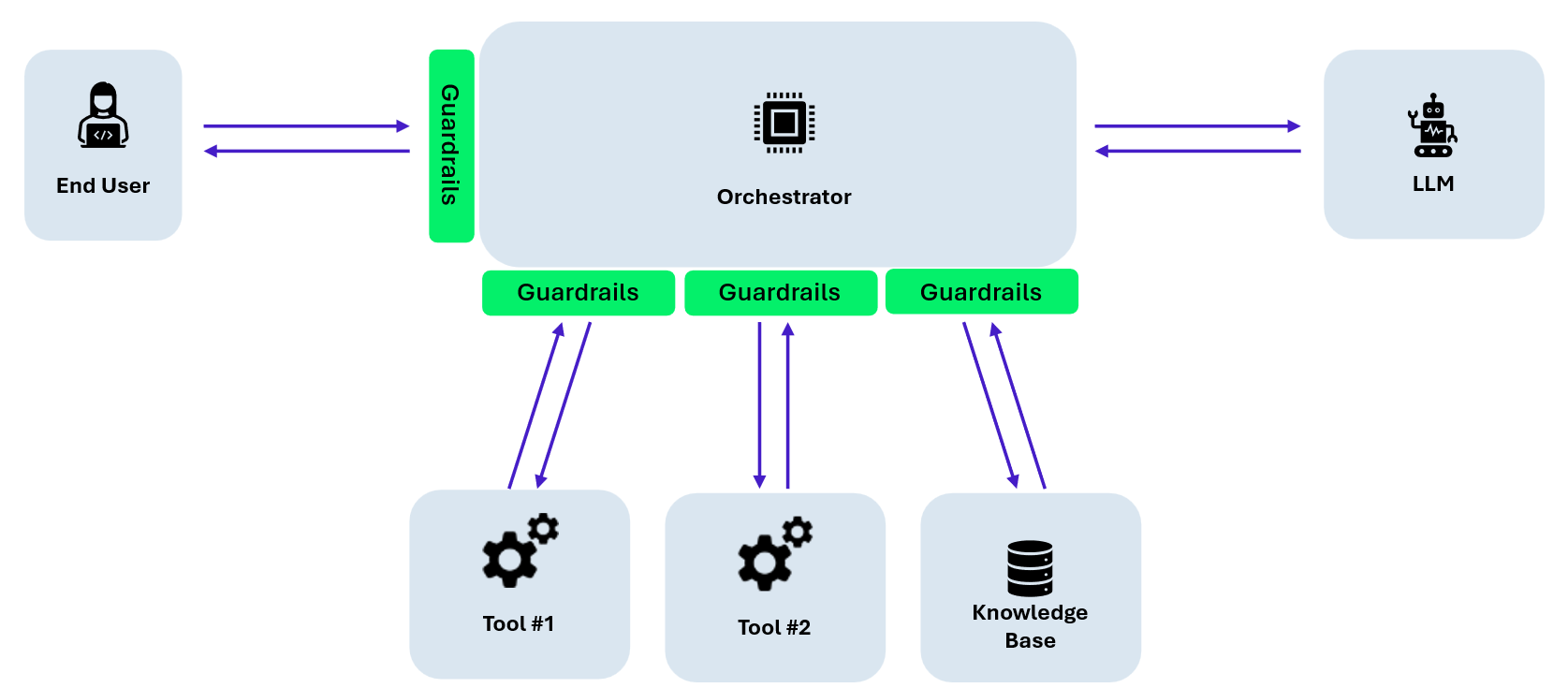
Customization
Beyond sensitivity tuning, fine-grained customization is essential for effective guardrails protections. Each application has specific filtering requirements, driven by business context, regulatory constraints, and threat exposure.
Personalization is required at multiple levels:
- Business context: blocking application-specific forbidden topics, such as competitors, confidential projects, or regulated information
- Threat mitigation: adapting filters to address high-impact attacks, including indirect prompt injection
- Data flow awareness: within a single application, different data sources require different filtering strategies. User inputs, retrieved documents, and tool outputs should not be filtered identically.
Applying uniform filtering across all inputs significantly limits effectiveness and may create blind spots. Guardrails must therefore be designed as part of the application architecture, not as a single monolithic filter.
Key Insights
This study highlights several key insights:
- No single guardrails solution fits all use cases, trade-offs exist between ease of deployment, performance, and customization
- Cloud-native guardrails provide an effective and low-effort baseline for most cloud-hosted applications
- Advanced use cases require configurable solutions capable of adapting filtering logic to application context and data flows
Guardrails should be selected based on risk exposure, operational maturity, and long-term maintainability rather than raw detection scores alone.
Guardrails have become a necessary component of LLM-based applications, and a wide range of solutions is now available. Selecting the right guardrails requires identifying the solution that best aligns with an organization’s specific risks, constraints, and application architecture.
Depending on your profile we have several suggestions for you:
- If your application is already deployed in a cloud environment, using the guardrails provided by the cloud provider is a good solution.
- If you want better control over the filtering solution, deploying one of the open-source guardrails solutions may be the most suitable option.
- You want the best and have the capacity, you can issue an RFI or RFP to compare different solutions and select the most tailored to your needs.
Finally, guardrails alone are not sufficient to protect your applications. Secure LLM applications also rely on properly configured tools, strict IAM policies, and robust security architecture to prevent more severe exploitation scenarios.


