About the study: This study is based on publicly available data up to Q3 2023 and aims to outline the various active Vulnerability Disclosure initiatives within the 100 largest banks and the EU countries.
Bug Bounty? A Bug Bounty program is a crowdsourcing initiative wherein ethical hackers are rewarded by companies for finding and reporting vulnerabilities.
In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, the banking and public sectors have increasingly embraced various vulnerability disclosure initiatives. Reflecting on Wavestone’s 2021 report, it’s crucial to understand the three key approaches that shaped the previous research:
- Vulnerability Report Channels (VRCs): These are the first step toward a bug bounty program, a web page providing basic instructions to hackers and a reporting channel.
- Vulnerability Disclosure Policies (VDPs): These policies outline how an organization receives and responds to disclosed vulnerabilities from external parties. The existence of a VDP implies the presence of a VRC as part of its framework.
- Bug Bounty Programs (BBPs): An advanced form of VDPs, and alongside the policy, BBPs offer financial rewards for reporting security vulnerabilities, incentivizing the discovery and disclosure of security issues. It can be accessible to anyone (public) or a small number of hackers (private).
These initiatives are not just procedural but bring significant benefits. They enable earlier detection of vulnerabilities, foster a culture of transparency and continuous improvement, and leverage the global cybersecurity community’s expertise to enhance security measures. By incentivizing ethical hacking, organizations can stay one step ahead of potential threats, protecting their data and systems more effectively.
Overview of Research
This study, leveraging data up to Q3 2023, examines the adoption and impact of these cybersecurity measures in the banking and public sectors. The research methodology involves a thorough analysis of current trends, regulatory landscapes, and the effectiveness of BBPs in enhancing digital security.
Banking sector insights
The banking sector, serving as the backbone of the global financial system, has shown a remarkable transformation in its approach to cybersecurity. The analysis of the world’s top 100 banks between 2020 and 2023 reveals significant developments in the adoption of cybersecurity measures. Here are some key insights:
- Increase of VRCs and VDPs: There was a marked increase in the implementation of VRCs and VDPs, by 2023, 34% of the top 100 banks had at least one active VRC, and 26% had implemented a VDP.
- Geographical Trends:
- Dominance in Europe and North America: Banks located in the United States and European countries demonstrated higher adoption rates of VRCs and VDPs. Delving deeper into the continent analysis, Figure 1 shows that North America, with 72% of banks implementing VRCs against Europe’s 49%, continues to be ahead in adopting cybersecurity initiatives.
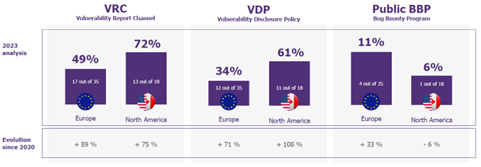
-
- Asia and South America: Despite managing 46% of the assets across 43 banks, only one implemented a VDP, indicating a slower pace of adopting for these kinds of programs.
- Stale number of Public BBPs: The data showed a stagnation in the number of public BBPs, with only 5% of the banks operating a public BBP as of 2023. This suggests a cautious approach towards publicly inviting vulnerability disclosures.
- Notable Countries: The Netherlands stands out with a 100% adoption rate of vulnerability disclosure programs among its top banks. This demonstrates a strong national commitment to cybersecurity.
- Platform Utilization: Most banks preferred developing in-house programs for vulnerability disclosure, with a few opting for external platforms like BugCrowd, Synack, and HackerOne.
Luxembourg: A Case Study
Luxembourg’s banking sector case study focused on 5 retail and 17 private banks, provides a snapshot of current cybersecurity practices:
- Overall low Adoption Rates: Only a minority of the 22 banks have embraced structured cybersecurity programs. Specifically, only 7 out of 22 banks have established VRCs, including only 5 banks which adopted VDPs and just 1 bank which implemented a Public BBP.
- External hacker Interest: Some banks received external reports through OpenBugBounty.org, demonstrating hackers’ interest in showing vulnerabilities, despite not having a formal active program.
- Overall Trend: The sector shows a need for more consistent adoption of structured cybersecurity strategies, especially considering the high stakes in private banking.
Public Sector Analysis and Regulation
The public sector’s approach to cybersecurity, especially within the EU27, shows a complex and evolving landscape. Key aspects of this analysis include: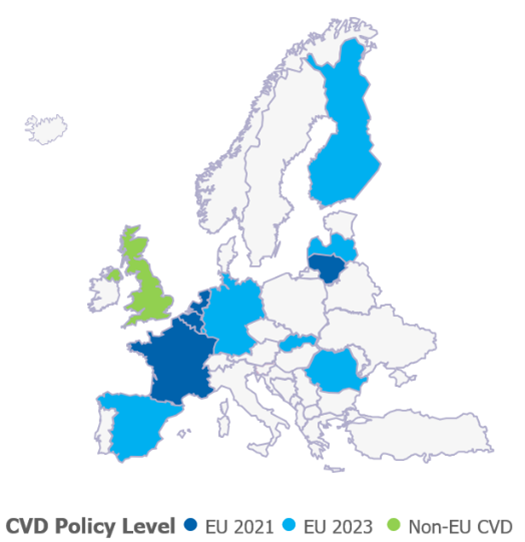
- Growth in Coordinated Vulnerability Disclosure (CVD): Compared with ENISA’s 2021 study, there has been a significant increase in the adoption of active CVD policies. The number of EU27 Member States with active CVD has risen from 4 to 11, indicating a growing emphasis on structured cybersecurity strategies.
- The UK’s Proactive Stance: Despite being outside the EU27, the United Kingdom has made remarkable efforts in implementing active CVD. This highlights the UK’s commitment to maintaining robust cybersecurity standards.
Conclusion and Future Outlook
As the digital world advances, the significance of vulnerability disclosure programs is increasingly clear. They represent not just a trend, but a fundamental shift in how organizations approach cybersecurity:
- The Rise of Vulnerability Disclosure: A dynamic and rapidly expanding area, these programs are becoming essential in the banking and public sectors.
- European Regulatory Momentum: With the EU’s NIS2 directive and forthcoming legislations like the CRA, there is a robust push for national CVD policies and organizational VDPs/BBPs.
At Wavestone, we understand the importance of staying ahead in this evolving scenario. We are here to help you navigate these changes effectively. Reach out to us for expert guidance in strengthening your cybersecurity position.


